Algorithm
树(Tree)
树是一种由n个节点构成的树形结构。
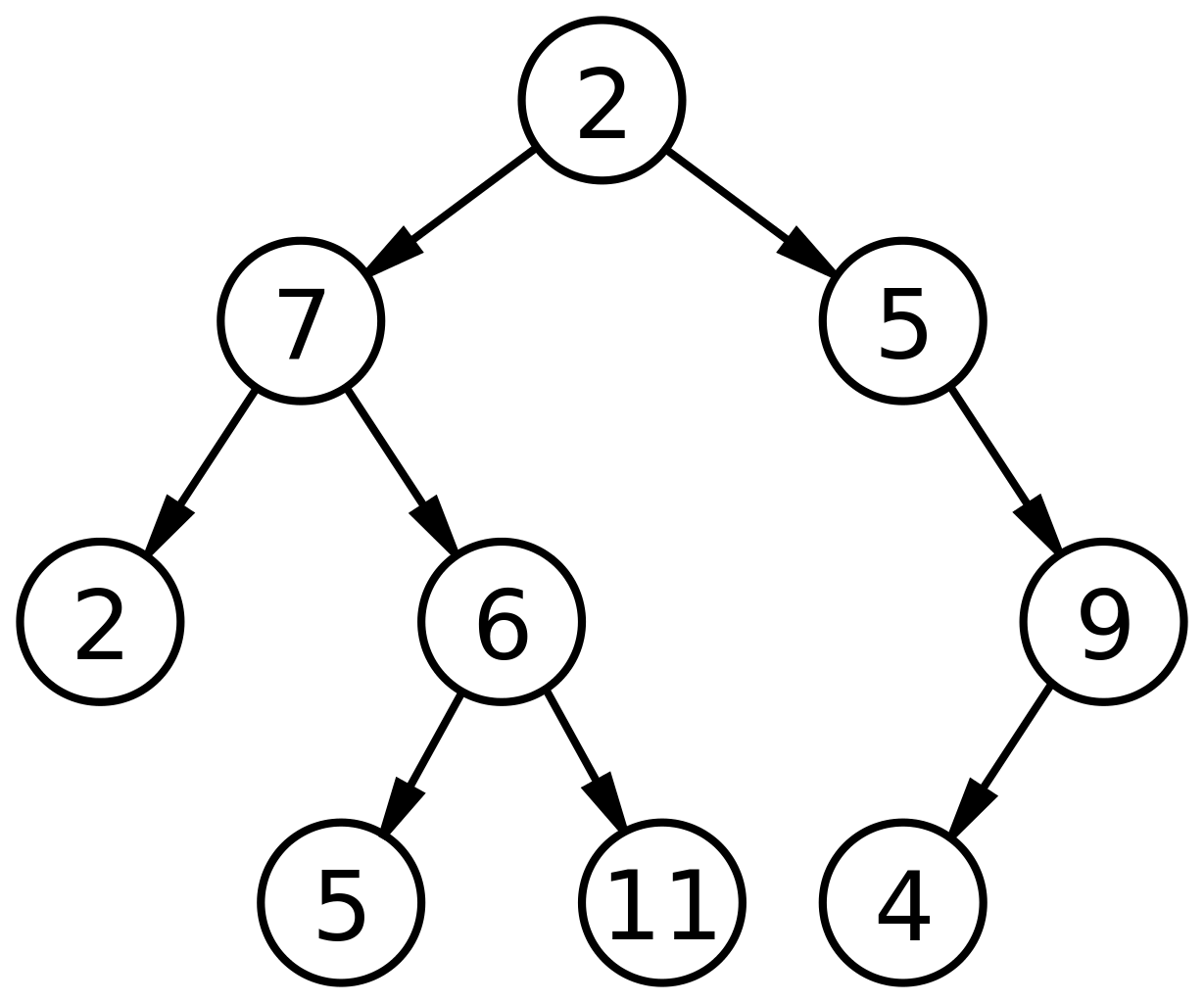
与生物学意义上的树不太相同,对于数据结构意义上的树来说,树的根在顶部,叶子则在底部。数据都存储在树的节点当中,节点除了数据之外还存储指向其父节点和子节点的指针–这和双向链表非常相似。通常,一个树只有一个父节点,但可能有多个子节点。我们将每个节点都有不超过m个子结点的树称之为m叉树。此外,倘若一个树的节点之间存在顺序关系,我们称其为有序树,反之则称其为无序树。对于一个树而言,我们将其第一个节点称作根节点(root node);将没有任何子节点的节点成为叶节点(leaf node);将由根节点到叶节点的最长距离称为树的高度h。下图是一个典型的高度为4的二叉搜索树:
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST)
通常,我们提到树或者二叉树时,我们指的其实是二叉搜索树,其影响力之大可见一斑。在本章当中,除非特别声明,否则当我们提到树时,我们指的也是二叉搜索树。二叉搜索树是一种二叉(即每个节点都有最多两个子节点)的有序树。他的实现非常简单:
二叉搜索树
Python @functools . total_ordering
class Data ( object ):
def __init__ ( self , value = None ):
self . value = value
def __eq__ ( self , other ):
return self . value == other . value
def __lt__ ( self , other ):
return self . value < other . value
class Node ( object ):
def __init__ ( self , parent = None , value = None , left_child = None , right_child = None ):
self . parent = parent
self . data = Data ( value )
self . left_child = left_child
self . right_child = right_child
class Tree ( object ):
def __init__ ( self ):
self . root = Node ()
def insert ( self , curr , value ):
self . insert_node ( root , value )
def delete ( self , value ):
self . delete_node ( root , value )
def height ( self ):
reutrn height_node ( root )
def height_node ( node ):
return 0 if not node else max ( height_node ( node . left_child ), height_node ( node . right_child )) + 1
理想情况下,二叉搜索树的深度应当是\(\log n\) 。由以上的实现我们可以得知二叉搜索树的查找、插入、删除的复杂度均为\(O(h)\) ,我们可以发现二叉搜索树的理想复杂度是很出色的。但是,事情通常不会按照预料之中发展。在极端情况之下(每一个新插入的元素都比之前的元素更小或更大),二叉搜索树即退化成了链表。我们知道,链表的复杂度为\(O(n)\) ,这很明显并不是我们想要的,于是,自平衡二叉树(Self-balacing Binary Search Tree)诞生了。
插入
插入
插入对于一棵自平衡二叉树来说挺难,但对一棵二叉搜索树来说还是很简单的。我们只需要根据新值的大小找到一个合适的位置即可。
Python @staticmethod
def insert_node ( node , value , parent = None ):
if not node :
node = Node ( parent , value )
else :
insert_node ( node . left_child , value , node ) if value < node . data . value else insert_node ( node . right_child , value , node ) if value > node . data . value else raise Exception ( 'Element already exists' )
遍历
树的遍历
作为一种非线性数据结构,从树的任一节点出发都有多个可以前往的下一节点,因此,树的遍历自然也比线性数据结构的遍历要高大上许多。
通常来说,我们有两种遍历思想–深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索。
深度优先搜索(Depth-First Search, DFS)
深度优先搜索先访问子节点,再访问父节点,随后再访问下一个子节点。
广度优先搜索的方式
由于深度优先遍历既可以先访问根,又可以先访问子节点。所以深度优先搜索也有不同的分支,他们是:
前序遍历(Pre-Order Traversal)
前序遍历
前序遍历先访问根,再访问子树。
Python @staticmethod
def pre_order ( node ):
# Do something with root
if node . left_child :
pre_order ( node . left_child )
if node . right_child :
pre_order ( node . right_child )
中序遍历(In-Order Traversal)
中序遍历
前序遍历先访问左(右)子树,再访问根,最后访问右(左)子树。
Python @staticmethod
def in_order ( node ):
if node . left_child :
in_order ( node . left_child )
# Do something with root
if node . right_child :
in_order ( node . right_child )
后序遍历(Post-Order Traversal)
前序遍历
前序遍历先访问子树,再访问根。
Python @staticmethod
def post_order ( node ):
if node . left_child :
post_order ( node . left_child )
if node . right_child :
post_order ( node . right_child )
# Do something with root
广度优先搜索(Breadth-First Search, BFS)
与深度优先搜索的花哨方式不同,广度优先搜索自顶向下完成遍历,自然有且只有一种可能。
广度优先搜索
Python def bredth_first ():
if not self . root :
return False
queue = []
queue . append ( self . root )
while ( len ( queue ) > 0 ):
# Do something with root
node = queue . pop ( 0 )
if node . left_child :
queue . append ( node . left_child )
if node . right_child :
queue . append ( node . right_child )
删除
删除
删除相对来说要比插入更为复杂一些。对于叶节点来说简单移去即可,对于只有一个子节点的节点来说,将指针转一下也很简单。但对于有两个子节点的节点来说,我们需要在树中找到一个新的既大于左子节点而又小于右子节点的值。乍看之下很难,实际上我们只需找到这个值以左(右)子节点构成的子树中最大(小)的值。
Python @staticmethod
def minimum_node ( node ):
curr = node
while curr . left_child :
curr = curr . left_child
return curr
@staticmethod
def delete_node ( node , value ):
if not node :
raise Exception ( 'Element does not exist' )
if value < node . data . value :
delete_node ( node . left_child , value )
elif value > node . data . value :
delete_node ( node . right_child , value )
else :
if not node . left_child :
node = node . right_child if node . right_child else None
elif not node . right_child :
node = node . left_child
else :
right_minimum = self . minumum_node ( node . right_child )
node . data . value = right_minimum . data . value
right_minimum = None
遍历练习
回忆例图中的二叉搜索树:
其先序遍历、中序遍历以及后序遍历的输出分别是多少?
答案
前序遍历 2 7 2 6 5 11 5 9 4
中序遍历 2 7 5 6 11 2 5 4 9
后序遍历 2 5 11 6 7 4 9 5 2
tree.pdf